Blood Pressure




Find a wide range of effective blood pressure medications and supplements designed to help manage hypertension and support heart health. Shop trusted brands and affordable options to maintain your well-being.
Blood pressure management is crucial for preventing heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Many medications help control high blood pressure effectively. Below is a review of popular drugs in this category. These medicines vary by mechanism, side effects, and dosing.
Aceon (perindopril) is an ACE inhibitor. It relaxes blood vessels and lowers blood pressure. Aceon is effective for long-term use. Side effects may include cough, dizziness, or elevated potassium. It is often prescribed alone or with other drugs.
Adalat (nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker. It widens blood vessels, reducing pressure. Adalat can be immediate or extended-release. Common side effects include flushing, headache, and swelling of ankles. It works well for isolated systolic hypertension.
Aldactone (spironolactone) is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It reduces fluid buildup, easing blood vessel strain. Aldactone is also used for heart failure and conditions with excess aldosterone. Side effects include increased potassium and breast tenderness in men.
Altace (ramipril) is another ACE inhibitor. It helps prevent heart attacks and strokes. Altace is often preferred after heart surgery. Side effects resemble other ACE inhibitors: persistent cough and dizziness. It also protects kidney function.
Avapro (irbesartan) belongs to ARBs (angiotensin II receptor blockers). It lowers blood pressure by blocking Angiotensin II effects. Avapro does not cause cough, a common issue with ACE inhibitors. It is useful for diabetic patients with kidney damage.
Beloc (metoprolol) is a beta-blocker. It slows heart rate and reduces force of contraction. Beloc lowers blood pressure and treats angina. Side effects include fatigue, cold hands, and sometimes sexual dysfunction. It is a standard choice for heart-related hypertension.
Benicar (olmesartan) is an ARB. It gently reduces arterial pressure. Benicar is effective in patients not tolerating ACE inhibitors. It may cause dizziness or elevated potassium. Benicar is often combined with diuretics for better control.
Calan (verapamil) and Calan SR are calcium channel blockers. They help relax heart and vessel muscles. Calan is suitable for patients with arrhythmias and high blood pressure. Side effects may include constipation and swelling. Calan SR is a slow-release version for convenient dosing.
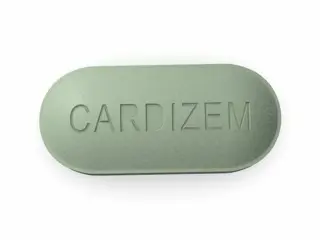
Cardizem (diltiazem) is a calcium channel blocker with effects on heart rhythm. It lowers blood pressure and controls chest pain. Cardizem slows heart rate, so it requires careful monitoring. Side effects can include fatigue and edema.
Cartia XT is an extended-release form of diltiazem. It offers stable blood levels, reducing side effects. It is useful for patients needing round-the-clock blood pressure control.
Catapres (clonidine) works in the brain to decrease nerve signals. It lowers heart rate and pressure. Catapres is often used when other drugs don't suffice. Side effects can include dry mouth, dizziness, and sedation. It may cause rebound hypertension if stopped abruptly.
Clonidine is also prescribed for ADHD and withdrawal symptoms. Its blood pressure effect is strong but needs monitoring.
Combipres contains clonidine and a diuretic. This combination helps lower pressure and reduce fluid retention. It can be effective for resistant hypertension but carries combined side effects.
Coreg (carvedilol) is both a beta-blocker and alpha-blocker. It lowers blood pressure and heart workload. Coreg is used in heart failure and high blood pressure. Side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and weight gain.
Coversyl (perindopril) is an ACE inhibitor similar to Aceon. It supports heart health and lowers pressure steadily. Coversyl is well-tolerated, with the common ACE inhibitor side effect of cough.
Cozaar (losartan) is an ARB. It relaxes blood vessels without causing cough. Cozaar protects kidneys in diabetes and is widely prescribed. Side effects include dizziness and increased potassium.
Diltiazem is available in several brands. It controls blood pressure and certain arrhythmias. Like other calcium channel blockers, watch for swelling and heart rate changes.
Esidrix (hydrochlorothiazide) is a thiazide diuretic. It helps eliminate excess salt and water. Esidrix is often first-line therapy for hypertension. Side effects include low potassium and increased urination.
Frumil combines a loop diuretic and potassium-sparing diuretic. It provides strong diuresis without major potassium loss. Useful in severe fluid retention cases alongside resistant hypertension.
Hytrin (terazosin) is an alpha-blocker. It relaxes blood vessels and improves urine flow in prostate issues. Hytrin lowers blood pressure but may cause dizziness, especially at first dose.
Hyzaar combines losartan and hydrochlorothiazide. It provides dual action to lower blood pressure effectively. Ideal for patients needing combination therapy. Side effects relate to both components.
Inderal (propranolol) is an older beta-blocker. It reduces heart rate and blood pressure. Inderal is well studied but may cause fatigue and cold extremities.
Inderal LA is a long-acting form of propranolol. It allows once-daily dosing and smoother blood pressure control.
Isoptin (verapamil) and Isoptin SR are calcium channel blockers. They reduce heart workload and relax arteries. Useful for hypertension and angina. Side effects include constipation and low heart rate.
Lasix (furosemide) is a loop diuretic. It causes strong diuresis and is used in fluid overload and hypertension. Side effects include low potassium and dehydration.
Lisinopril is a common ACE inhibitor. It lowers pressure and protects kidneys. Side effects include cough and rare angioedema. It’s used alone or in combinations.
Lopressor (metoprolol tartrate) is a beta-blocker controlling heart rate and pressure. Side effects include tiredness and cold hands. It usually requires twice-daily dosing.
Lozol (indapamide) is a thiazide-like diuretic. It removes excess fluid and lowers blood pressure. It has a longer duration than standard thiazides.
Micardis (telmisartan) is an ARB. It provides long-lasting blood pressure control. Micardis is favored for once-daily use and kidney protection. Side effects include dizziness and elevated potassium.
Microzide (hydrochlorothiazide) is a widely used diuretic. It helps reduce blood volume and pressure. Watch for low potassium and increased urination.
Minipress (prazosin) is an alpha-blocker relaxing blood vessels. It helps with hypertension and symptoms of an enlarged prostate. Side effects include dizziness and headache at treatment start.
Norvasc (amlodipine) is a calcium channel blocker with once-daily dosing. It is effective and well-tolerated. Common side effects include swelling of hands and feet and flushing.
Prinivil (lisinopril) is an ACE inhibitor similar to others in the class. It reduces pressure and protects heart and kidneys. Side effects may include cough and fatigue.
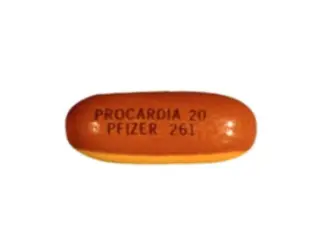
Procardia (nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker. It rapidly lowers blood pressure. Procardia XL is a slow-release form for stable control. Side effects include headache, flushing, and swelling.
Tenormin (atenolol) is a beta-blocker. It decreases heart rate and pressure. It requires caution in asthma patients. Side effects may include tiredness and cold extremities.
Toprol (metoprolol succinate) is an extended-release beta-blocker. It controls blood pressure and heart rhythm. Used in heart failure and hypertension. Side effects include fatigue and dizziness.
Toprol XL offers once-daily dosing for better adherence and stable drug levels. It shares side effects with other beta-blockers.
Trandate (labetalol) blocks beta and alpha receptors. It lowers blood pressure and is used in hypertension crises. Side effects include dizziness and fatigue.
Tritace (ramipril) is an ACE inhibitor protecting the heart and kidneys. It reduces stroke risk and improves survival after heart attack. Side effects include cough and low blood pressure.
Vasotec (enalapril) is a common ACE inhibitor. It reduces pressure and protects organs. Side effects include cough and high potassium levels.
Verampil (verapamil) is a calcium channel blocker used to lower blood pressure and control arrhythmias. It can cause constipation and low heart rate.
Verapamil works well for patients with high blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms. SR versions provide steady drug levels.
Zebeta (bisoprolol) is a beta-blocker with cardioselective properties. It reduces heart rate and pressure. It is well tolerated with fewer respiratory side effects.
Zestoretic combines lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. This mix targets blood vessels and fluid excess simultaneously. It is effective for multi-mechanism hypertension.
Zestril (lisinopril) offers blood pressure control and cardiovascular protection. Side effects include cough and dizziness, typical for ACE inhibitors.
Each blood pressure medication offers different benefits and risks. The choice depends on patient health, other conditions, and tolerance. Combining drugs often achieves the best control. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting or changing treatment.